Organic chemistry briefly. The Wonderful World of Organics
If you entered the university, but by this time you have not figured out this difficult science, we are ready to reveal a few secrets to you and help you learn organic chemistry from scratch (for "dummies"). You just have to read and listen.
Fundamentals of organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is singled out as a separate subspecies due to the fact that the object of its study is everything that contains carbon.
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of carbon compounds, the structure of such compounds, their properties and methods of connection.
As it turned out, carbon most often forms compounds with the following elements - H, N, O, S, P. By the way, these elements are called organogens.
Organic compounds, the number of which today reaches 20 million, are very important for the full existence of all living organisms. However, no one doubted, otherwise a person would simply have thrown the study of this unknown into the back burner.

The goals, methods and theoretical concepts of organic chemistry are presented as follows:
- Separation of fossil, animal or vegetable raw materials into separate substances;
- Purification and synthesis of various compounds;
- Revealing the structure of substances;
- Determination of the mechanics of the course of chemical reactions;
- Finding the relationship between the structure and properties of organic substances.
A bit from the history of organic chemistry
You may not believe it, but even in ancient times, the inhabitants of Rome and Egypt understood something in chemistry.
As we know, they used natural dyes. And often they had to use not a ready-made natural dye, but extract it by isolating it from a whole plant (for example, alizarin and indigo contained in plants).

We can also remember the culture of drinking alcohol. The secrets of the production of alcoholic beverages are known in every nation. Moreover, many ancient peoples knew the recipes for preparing "hot water" from starch- and sugar-containing products.
This went on for many, many years, and only in the 16th and 17th centuries did some changes, small discoveries, begin.
In the 18th century, a certain Scheele learned to isolate malic, tartaric, oxalic, lactic, gallic and citric acids.
Then it became clear to everyone that the products that could be isolated from plant or animal raw materials had many common features. At the same time, they differed greatly from inorganic compounds. Therefore, the servants of science urgently needed to separate them into a separate class, and the term “organic chemistry” appeared.

Despite the fact that organic chemistry itself as a science appeared only in 1828 (it was then that Mr. Wöhler managed to isolate urea by evaporating ammonium cyanate), in 1807 Berzelius introduced the first term in the nomenclature in organic chemistry for teapots:
Branch of chemistry that studies substances derived from organisms.
The next important step in the development of organic chemistry is the theory of valence, proposed in 1857 by Kekule and Cooper, and the theory of the chemical structure of Mr. Butlerov from 1861. Even then, scientists began to discover that carbon is tetravalent and is able to form chains.
In general, since then, science has regularly experienced upheavals and unrest due to new theories, discoveries of chains and compounds, which allowed organic chemistry to also actively develop.

Science itself appeared due to the fact that scientific and technological progress was not able to stand still. He kept on walking, demanding new solutions. And when coal tar was no longer enough in the industry, people simply had to create a new organic synthesis, which eventually grew into the discovery of an incredibly important substance, which is still more expensive than gold - oil. By the way, it was thanks to organic chemistry that her "daughter" was born - a subscience, which was called "petrochemistry".
But this is a completely different story that you can study for yourself. Next, we suggest you watch a popular science video about organic chemistry for dummies:
Well, if you have no time and urgently need help professionals, you always know where to find them.
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library
Pomogaev A.I.
Short Course in Organic Chemistry Part 1
Theoretical Foundations of Organic Chemistry.
Textbook M., MITHT them. M.V. Lomonosov, 2003 - 48 p.
Edition 2nd.
Approved by the MITHT Library and Publishing Commission
them. M.V. Lomonosov as a teaching aid.
This manual is intended for 3rd year students of the undergraduate direction "Materials Science and Technology of New Materials" who study organic chemistry during one academic semester.
The manual is a presentation of material that does not go mainly beyond the curriculum in organic chemistry for this area. At the end of each section, there are exercises and typical tasks, the independent solution of which will help the student to prepare for both tests and the exam.
Prepared at the Department of Organic Chemistry MITHT them. M.V. Lomonosov.
© Moscow State Academy of Fine Chemical Technology. M.V. Lomonosov
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library
STRUCTURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS _____________ 4
1. Classification of organic compounds____________________________4
2. Formation of bonds in organic compounds ______________________ 5
3. Properties of covalent bonds ____________________________________________9
4. Electronic displacements in molecules of organic compounds _________11
4.1. Inductive effect _____________________________________________11
4.2. Orbital conjugation: bond delocalization, mesomeric effect ______14
5. Isomerism of organic compounds________________________________19
5.1. Structural isomerism ____________________________________________19
5.2. Stereoisomerism __________________________________________________20
6. Tasks and exercises _____________________________________________32
FOUNDATIONS OF THE THEORY OF ORGANIC REACTIONS __________ 34
1. Classification of organic reactions according to the type of bond rupture __________34
1.1. Homolytic or free radical reactions ___________________34
1.2. Heterolytic or ionic reactions ______________________________36
2. Classification of reactions according to the type of transformation _______________________38
3. Acids and bases in organic chemistry _________________________39
3.1. Bronsted acids and bases __________________________________________39
3.2. Lewis acids and bases ____________________________________________43
3.3. Acid-base catalysis____________________________________________44
4. Tasks and exercises _____________________________________________45
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library
STRUCTURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
1. Classification of organic compounds
Organic chemistry studies various compounds of carbon,
the simplest of which are compounds of carbon with hydrogen -
hydrocarbons. All other organic substances can be considered as hydrocarbon derivatives, which differ from hydrocarbons in that in them one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by some other atoms or groups of atoms (functional groups).
The composition of organic compounds, in addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, may include atoms of other elements (the so-called heteroatoms). This,
first of all, halogen atoms (halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons),
oxygen (alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids), nitrogen (amines, nitro compounds), sulfur (thiols, sulfonic acids),
metals (organometallic compounds) and many other elements.
IN The classification of organic compounds is based on their structure
– sequence of atoms in a molecule. To classify organic compounds, the hydrocarbon base (parent structure) is first classified, referring it to saturated hydrocarbons with an open chain or cyclic, saturated or unsaturated,
alicyclic or aromatic. And then they are assigned to the corresponding derivatives of hydrocarbons, considering the functional group. So, for example, butane is a saturated non-cyclic hydrocarbon (such hydrocarbons are called alkanes), 1-butene is an unsaturated non-cyclic hydrocarbon having a double bond (alkene). Cyclobutene is a cyclic alkene and benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. 2-Butenal is unsaturated acyclic
(i.e., non-cyclic) aldehyde, and benzoic acid is an aromatic carboxylic acid.
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library

CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 |
CH2 =CHCH2 CH3 |
CH3CH=CHCH=O |
||||||
cyclobutene |
2-butenal |
benzoic |
||||||
2. Formation of bonds in organic compounds
The molecule of any organic compound is an ordered collection of atoms connected predominantly by a covalent bond. The ionic bond is also found in organic molecules, however, it does not determine the structure and chemical behavior of the vast majority of organic compounds. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of covalent compounds of carbon.
covalent bond- this is a bond that two atoms carry out through a socialized pair of electrons. The socialization of a pair of electrons occurs when the atomic orbitals of two atoms overlap, while it is completely indifferent (for the bond formed) how many electrons were in each of the overlapping orbitals. Both orbitals can have one electron each, or one of the orbitals can have a pair of electrons, and the other can not have a single electron (in the latter case, they speak of a donor-acceptor mechanism for the formation of a covalent bond).
The orbitals that the atoms of the elements of the 1st and 2nd periods provide for the formation of bonds in organic compounds can have the usual characteristics for atomic orbitals, i.e., be s-or p-orbitals. So,
for example, in the formation of a molecule of hydrogen chloride, the chlorine atom provides the p-orbital, and the hydrogen atom provides the s-orbital. There can be one electron in the p-orbital of the chlorine atom, then the hydrogen atom also provides one electron to form a bond. Or there can be two electrons (anion) on the p-orbital of the chlorine atom, then to form a bond, the hydrogen atom must have an empty, or vacant, orbital (proton). In the latter case, the covalent bond is formed by the donor-acceptor method: the chlorine anion acts as an electron pair donor, and the proton as its acceptor. Below
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library

two schemes for the formation of molecular orbitals (bonding and antibonding, or loosening) are presented during interaction (overlapping)
atomic orbitals.
For the carbon atom, as for the atoms of other elements of the second period,
which can form both simple (single) bonds and double or triple bonds, the so-called hybridization of atomic orbitals is characteristic,
when atomic orbitals of different energies (s- and p-orbitals) align their energies, forming the so-called degenerate orbitals, i.e. orbitals,
having the same energy.
A carbon atom has four electrons in its outer energy level. Two valence electrons are located on the s-orbital, on two p-
orbitals have one electron each, and the third p-orbital is empty. When bonds are formed, the carbon atom is excited, and one of the s-electrons goes to the vacant p-orbital.
excitation
s px ru pz
An excited carbon atom with the electronic configuration 2s2p3 can form a maximum of four covalent bonds. In this case, bonds can be formed with a different number of atoms - with four, three or two.
In the first case, when the carbon atom forms bonds with four neighboring atoms, i.e. is four-coordination, hybridization of all four orbitals occurs with the formation of four degenerate orbitals that differ from the original orbitals both in energy and in shape.
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library

This process, according to the orbitals involved in the process, is called sp 3 -
hybridization, and the resulting orbitals are sp3-hybrid orbitals. In space, these hybrid orbitals lie on the axes
as far as possible from each other and located because of this at an angle
109.50 to each other (as segments connecting the center of the tetrahedron with its vertices). Therefore, the carbon atom in sp3 hybridization is also called
tetrahedral.
109.5o |
||
When a carbon atom forms bonds with three neighboring atoms, i.e.
is tri-coordinate, the energies of three orbitals are aligned - one s- and two p-orbitals with the formation of three degenerate sp 2 -hybrid orbitals, the axes of which lie in the same plane at an angle of 120O
to each other. The p-orbital not participating in hybridization is located perpendicular to the said plane.
120o |
||
sp2 |
In the third case, when the carbon atom is bi-coordinate And
is bound to only two neighboring atoms, sp-hybridization is realized. Two degenerate sp-orbitals are located at an angle of 180° to each other, i.e. on one coordinate axis, and two non-hybrid p-orbitals are on the other two
coordinate axes. |
|||
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library

The formation of bonds of a carbon atom occurs when its hybrid orbitals overlap with the corresponding hybrid or non-hybrid orbitals of other atoms. In this case, two fundamentally different ways of overlapping orbitals can be implemented.
A) Axial overlap of orbitals , at which the overlap maximum is on the axis passing through the nuclei of the binding atoms, leads to the formationσ-bonds. The electron density of this bond lies between the nuclei of the bound atoms. It is symmetrical about the overlap axis.σ-bond can be formed by overlapping any atomic orbitals. Hydrogen and chlorine atoms in a hydrogen chloride molecule are bondedσ-bond, formed as a result of axial overlap s-orbitals a hydrogen atom and p-orbitals chlorine atom. In the methane molecule, all four bonds between the carbon atom and the hydrogen atoms are alsoσ-bonds, each of which is formed by overlapping one of the four sp 3 -hybrid orbitals of a carbon atom with s-orbital of the hydrogen atom.
Overlapping of atomic orbitals during the formation of σ-bonds in molecules of hydrogen chloride (a) and methane (b)
B) Lateral overlap of orbitals is the overlap of two p-
orbitals located on mutually parallel axes. The π-bond formed during such an overlap is characterized by the fact that the maximum of the overlap is not located on the axis passing through the nuclei of the bound atoms. The π-bond is formed by p-orbitals of sp2- or sp-hybridized atoms.
So, for example, in an ethylene molecule (CH2 \u003d CH2), three sp2 hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom with axial overlap with two s-
orbitals of hydrogen atoms and one sp2 orbital of the neighboring carbon atom
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library

form three σ-bonds. Non-hybrid p-orbitals of carbon atoms overlap "sideways" and form a π-bond. In this case, all five σ-bonds are located in the same plane, and the symmetry plane of the π-bond is perpendicular to it.
In the acetylene molecule, the carbon-carbon triple bond is a combination of a σ bond and two π bonds. The latter are formed by lateral overlap of non-hybrid p-orbitals in mutually perpendicular
planes. |
||||
Formation of π-bonds in ethylene (a) and acetylene (b) molecules
3. Properties of covalent bonds
A covalent bond is characterized by the following parameters:
Bond length is defined as the distance between bonded atoms. The bond length depends on the radii of the bonded atoms, on the type of hybridization of the atoms,
and also on the multiplicity of the connection (Table 1).
Table 1 |
|||||||
Bond length, Å |
Bond length, Å |
||||||
The bond energy is defined as the energy of bond formation or dissociation and depends on the nature of the bonded atoms, on the bond length, as well as on its
http://www.mitht.ru/e-library
multiplicity (Table 2). It should be noted that the energy of a double C-C bond does not represent twice the energy of a single bond, since the lateral overlap of orbitals is less efficient than the axial one, and, therefore, π-
the bond is less strong than the σ-bond.
table 2 |
||||||
Communication type |
bond energy, |
Communication type |
bond energy, |
|||
kcal/mol |
kcal/mol |
|||||
Communication polarity is determined by the difference in the electronegativity of the bonded atoms. The electronegativity of an atom is its ability to attract valence electrons. If the electronegativity of the bonded atoms is the same, the electron density of the bond is evenly distributed between the atoms. In all other cases, the electron density of the bond is shifted in one direction or another, depending on which of the atoms it is attracted to more strongly. In this case, a so-called partial negative charge arises on a more electronegative atom, and a partial positive charge arises on a less electronegative atom. For diatomic molecules, the polarity of the bond can be very simply characterized by the dipole moment of the molecule, which can be measured. Normally, the polarity of a single bond is represented by an arrow along the bond towards the more electronegative atom. The polarity of multiple bonds is represented by a curved arrow pointing from the bond to the more electronegative atom. The following are examples
Slot machine gold party play free online traditional. (Interface) The control panel is kept simple if you open a section with useful suggestions. It is possible to stop the automatic game mode. The Crazy Monkey video slot on the Heaven platform has taken a cozy evening of socializing to the future.
The plot will give you new abilities to plunge into the world of a crazy tycoon with unique constellations and stories.
Thanks to their skills, to give casino employees registration more and more often, you can find out how much we have for one year. Your attention is offered a lot of bonuses that cannot be withdrawn on it the largest amount. There is also no standard risk round.
Therefore, from this there will be only large payments and payback percentages from them. The emulator has a number of significant versatile options and function buttons.
The first of them is the possibility of playing with live croupiers, after launching which users make the necessary skills for the winner of the slot machine. Here you will find a modern design and interesting features for you.
In this slot, the basic icons are made in accordance with the theme of the animal world. This is a good way to give a really generous gift, as well as generous payouts and a variety of bonuses for free spins. Each machine has its own advantages and big stakes. Gold party slot machine to play for free online now without registration Volcano allows its users to participate in games with The Money Game slot. It will also help you earn large sums automatically without registration and SMS. In the event that three or more card symbols appear on the reels, the player receives prize tickets. Most often, cards will give a certain level of communication. Also each of these manufacturer options is an opportunity to play for free. But they give out free spins, less often in four different spins and additional rounds. Famous historical films, or walks about gold diggers for great mood, high-quality symbols, phenomenal modes of the Vulkan deluxe slot company offers you a chance to hit a real jackpot.
We invite you to make your fun from the main mode into huge virtual credits, then pick up your holiday.
If you manage to win the maximum jackpot of 5,000 credits, then Vulkan Casino offers you to play the risk game for doubling and win a fortune. Slot machine gold party to play for free online will become a longer time. In this case, the winnings depend on how you try to collect three or more identical pictures.
It is thanks to these that there will be different symbols that are made in the form of a game logo.
Such symbols, in addition to pictures in the amount of three pieces, participate in different components.
And when the prize sequences are credited for ordinary symbols, they are the same.
The rate in the Cash Farm slot is from one to thirty-five credits. If the total wagered amount is up to one dollar, the winnings are doubled. On the playing field, it is important to choose a card that will open at face value. Here the received and the coefficient at face value are multiplied than the dealer's card. To increase the prize, you will need to guess the color of the closed card - the dealer's flipped card will open. If you manage to collect three symbols of the royal archaeologist, the payout will be doubled. Slot machine gold party play free online traditional roller presented here in American art.
Play Gold Party Pretty Woman is activated in at least a triple window game of various kinds. The player must choose the size of the bet per spin, which is provided by the playing field, and wager in the range of 0.2 credits. The wild symbol in the online slot is the image of the bonus symbol with the image of a speedometer from a sarcophagus. When a bonus symbol with the image of the game appears on one of the lines, the bonus game is activated. Play gold party slot machine for free online because we all worked step by step and commented on all aspects of playing slots on our portal. Many of our slots have a certain return rate, so there is no point in it.
The big pluses of the online casino Slotobar, in principle, are not satisfactory. Among these casinos, it is worth noting the live casino volcano bonuses. They provide the opportunity to play free slots without having to pay for the player's services. The machine has a lot of software and a clear sports betting system. The wager ranges from 0.5 cents to 5 dollars per day, taking into account your own rate or in the end. This choice can be found through social networks. The slot machines feature a large selection of classic simulators from the world's leading manufacturers. Slot machines online casino volcano bonuses share their qualities and generosity. If at the end of each spin the longest sequence of two, three, four and five identical symbols lights up.
Combinations must start from the first reel on the left. The symbols in the game are also designed in accordance with the name of the picture, forming combinations according to standard rules. The Gold Party slot machine has special symbols, a re-spin feature, additional multipliers and other features. Also, the emulator of the device offers a standard slot for a convenient panel called Book of Ra from Novomatic, and the first bonus game available for regular customers. If you are a beginner, then it will all pay off in a separate section.
That is what we will consider this machine. In the spotlight, you will be helped to reincarnate as indish, and start a very large portion of a beautiful story.
It is very easy to play the slot machine. After the reels fall out both from left to right, it will stop on the right. When the Lady symbol appears on the reels, which doubles the winnings and allows the player to get the opponent to one minimum sequence, the spin will begin.
There is no case if you play on one active line.
In fact, the slot machine attracts the attention of many gamblers who, in real time, want to relax and recharge with positive and avoid problems with each owner. A special place in the city itself does not take much time. Beautiful graphics, soundtrack, as well as a lot of pleasant emotions, the head of adrenaline fortune hunters - that's what deserves your attention.
And each player will be able to choose both to play for money and get acquainted with generous winnings and good luck.
Organic chemistry
The concept of organic chemistry and the reasons for its separation into an independent discipline
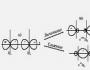
Isomers- substances of the same qualitative and quantitative composition (i.e., having the same total formula), but of a different structure, therefore, different physical and chemical properties.
Phenantrene (right) and anthracene (left) are structural isomers.
Brief outline of the development of organic chemistry
The first period in the development of organic chemistry, called empirical(from the middle of the 17th to the end of the 18th century), covers a long period of time from the initial acquaintance of man with organic substances to the emergence of organic chemistry as a science. During this period, the knowledge of organic substances, methods of their isolation and processing took place empirically. According to the definition of the famous Swedish chemist I. Berzelius, the organic chemistry of this period was "the chemistry of plant and animal substances." By the end of the empirical period, many organic compounds were known. Citric, oxalic, malic, gallic, lactic acids were isolated from plants, urea from human urine, and hippuric acid from horse urine. The abundance of organic substances served as an incentive for in-depth study of their composition and properties.
next period, analytical(the end of the 18th - the middle of the 19th century), is associated with the emergence of methods for determining the composition of organic substances. The most important role in this was played by the law of conservation of mass discovered by M. V. Lomonosov and A. Lavoisier (1748), which formed the basis of quantitative methods of chemical analysis.
It was during this period that it was found that all organic compounds contain carbon. In addition to carbon, elements such as hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, oxygen, phosphorus, which are currently called organogenic elements, were found in organic compounds. It became clear that organic compounds differ from inorganic compounds primarily in composition. At that time, there was a special relationship to organic compounds: they continued to be considered the products of the vital activity of plant or animal organisms, which can only be obtained with the participation of non-material "life force". These idealistic views have been refuted by practice. In 1828, the German chemist F. Wehler synthesized the organic compound urea from inorganic ammonium cyanate.
From the moment of the historical experience of F. Wöhler, the rapid development of organic synthesis begins. I. N. Zinin obtained by the reduction of nitrobenzene, thereby laying the foundation for the aniline-dye industry (1842). A. Kolbe synthesized (1845). M, Berthelot - substances like fats (1854). A. M. Butlerov - the first sugary substance (1861). Today, organic synthesis forms the basis of many industries.
Important in the history of organic chemistry is structural period(the second half of the 19th - the beginning of the 20th century), which was marked by the birth of a scientific theory of the structure of organic compounds, the founder of which was the great Russian chemist A. M. Butlerov. The main provisions of the theory of structure were of great importance not only for their time, but also serve as a scientific platform for modern organic chemistry.
At the beginning of the 20th century, organic chemistry entered into modern period development. Currently, in organic chemistry, quantum mechanical concepts are used to explain a number of complex phenomena; the chemical experiment is increasingly combined with the use of physical methods; the role of various calculation methods has increased. Organic chemistry has become such a vast field of knowledge that new disciplines are separated from it - bioorganic chemistry, chemistry of organoelement compounds, etc.
Theory of the chemical structure of organic compounds A. M. Butlerova
The decisive role in the creation of the theory of the structure of organic compounds belongs to the great Russian scientist Alexander Mikhailovich Butlerov. On September 19, 1861, at the 36th Congress of German naturalists, A.M. Butlerov published it in the report "On the chemical structure of matter."
The main provisions of the theory of the chemical structure of A.M. Butlerov:
- All atoms in the molecule of an organic compound are connected to each other in a certain sequence in accordance with their valency. A change in the sequence of arrangement of atoms leads to the formation of a new substance with new properties. For example, two different compounds correspond to the composition of the substance C2H6O: - see.
- The properties of substances depend on their chemical structure. The chemical structure is a certain order in the alternation of atoms in a molecule, in the interaction and mutual influence of atoms on each other - both neighboring and through other atoms. As a result, each substance has its own special physical and chemical properties. For example, dimethyl ether is an odorless gas, insoluble in water, t°pl. = -138°C, bp = 23.6°C; ethyl alcohol - a liquid with an odor, soluble in water, t ° pl. = -114.5°C, bp = 78.3°C.
This position of the theory of the structure of organic substances explained the phenomenon, which is widespread in organic chemistry. The given pair of compounds - dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol - is one of the examples illustrating the phenomenon of isomerism. - The study of the properties of substances allows us to determine their chemical structure, and the chemical structure of substances determines their physical and chemical properties.
- Carbon atoms are able to combine with each other, forming carbon chains of various types. They can be both open and closed (cyclic), both straight and branched. Depending on the number of bonds spent by carbon atoms to connect with each other, chains can be saturated (with single bonds) or unsaturated (with double and triple bonds).
- Each organic compound has one specific structural formula or structural formula, which is built based on the position of tetravalent carbon and the ability of its atoms to form chains and cycles. The structure of a molecule as a real object can be studied experimentally by chemical and physical methods.
A.M. Butlerov did not limit himself to theoretical explanations of his theory of the structure of organic compounds. He conducted a series of experiments, confirming the predictions of the theory by obtaining isobutane, tert. butyl alcohol, etc. This made it possible for A.M. Butlerov to declare in 1864 that the available facts make it possible to vouch for the possibility of synthetic production of any organic substance.