DC welding machine for four posts. Inverter: DC or AC? How to make the most convenient transformer for welding: practical tips
Do-it-yourself direct and alternating current does not take much time and effort.
The main condition for its creation is a clear idea of what kind of welding work it should perform and instructions.
To carry out welding, you need a device that operates on AC and DC.
The current apparatus welds thin metal sheets. This welding method does not require the use of a specific type of electrode, and the electrode wire can be without ceramic coating.
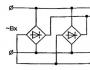
The scheme of the welding machine consists of 5 parts. The current circuit passes through the welding machine, first entering the transformer.
From there, the current flows into the rectifier, the diodes of which convert the alternating current into direct current, and the inductor. The last elements of the current flow are the holder and the electrode.
The electrode holder is connected to the rectifier using a choke. This smooths out the voltage pulse.
A choke is a coil of copper wire wound around a core. And the rectifier is a part of the apparatus connected to the transformer through the secondary winding.
A transformer is connected to the network - the main part of the device. It can either be specially purchased, or you can use a previously operated, but suitable transformer.
It converts AC voltage according to Ohm's law.

So the indicator of the voltage generated on the secondary winding decreases, but at the same time the current strength increases by 10 times. Welding occurs at a current of 40 amperes.
The electrical circuit closes at the moment when an arc appears between the electrode and the pieces of metal being welded.
The arc must burn stably, then the weld will be made with high quality. In establishing the desired nature of combustion will help the power regulator of electrical energy.
The most elementary scheme of the unit
It is better if the electrical circuit of the unit is the most elementary.
An easy-to-assemble device, assembled by oneself, must be connected to an AC voltage of 220 volts.
A voltage of 380 volts requires a more complex design of the welding machine.
The simplest circuit is the circuit for the pulse welding method, which was invented by radio amateurs. Such welding is used to attach wires to a metal board.
To build this device with your own hands, you do not need to do anything complicated, you only need a couple of wires and a choke. The inductor can be removed from the fluorescent lamp.
The current regulator can be replaced with a fusible link. It is better to stock up on wires in large quantities.
To connect the electrode to the board, a choke is taken. The electrode can be a crocodile clip. The finished unit must be connected to the network by plugging the plug into the outlet.

With a clamp connected to the wire, you need to quickly touch the welded area on the board.
This is how the welding arc appears. During its occurrence, there is a danger that the fuses located in the electrical panel will burn out.
Fuses are protected from this danger by a fusible link that burns out faster.
As a result, the wire remains still welded to its place.
Such a DC device is the simplest welding machine. It is connected to the electrode holder by wires.
But it seems possible to work with it only at home, since this circuit is devoid of important details - a rectifier and a current regulator.
Complete set of the unit for welding
In comparison with traditional devices, a three-phase inverter type unit is compact, convenient to use, and reliable. Only one nuance makes you think at the time of purchase - a rather big price.
Even superficial calculations suggest that making a welding machine with your own hands will come out cheaper.
If you approach the choice of the necessary elements with all seriousness, then a home-made welding tool will last a long period of time.
In general, the circuit of the welding machine consists of three blocks: a rectifier unit, a power supply unit and an inverter unit.
A home-made DC and AC apparatus can be completed so that it can be light in weight and have a small size.
A home-made welding machine is easily built with your own hands, using objects available to everyone.
All the parts necessary to create a welding unit are in electrical engineering or in devices where some elements have failed to work.
It is possible to build a simple current regulator from a part of a heating coil used in an electric stove.
If some necessary details could not be found at all, then it's okay - you can do them yourself.
A piece of copper wire can serve as a material for creating such an important element of a DC and AC welding machine as a choke.
Specifically, for its assembly, you will need a magnetic circuit, which has an old starter. You also need 2-3 copper wires with a cross section of 0.9 - and you can get a choke.
The transformer for the welding unit can be an autotransformer or the same part taken from an old microwave oven.
When taking out the necessary element from it, you need to be careful not to spoil the primary winding.
And the secondary will have to be redone anyway, the number of new turns depends on how much power the unit is being designed.
The rectifier is assembled on a board made either from getinax or textolite.
Diodes for the rectifier must correspond to the selected power of the unit. To keep them cool, an aluminum alloy radiator is used.
Consistent assembly of all parts
All elements of the unit for welding must be located on a metal or textolite base strictly in their places.
According to the rules, the rectifier borders on the transformer, and the inductor is located on the same board as the rectifier.
The current regulator is installed on the control panel. The frame itself for the construction of the unit is created from aluminum sheets, steel is also suitable for this.
You can also use a ready-made case, which previously protected the contents of the system unit of a computer or oscilloscope. Most importantly, it must be strong and durable.
At a great distance from the transformer, a board with thyristors is placed. Also, a rectifier is not installed close to the transformer.
The reason for this arrangement is the strong heating of the transformer and inductor.
Heat is removed from the inductor by thyristors mounted on aluminum radiators. They negate even the heat waves emanating from the wires.
An electrode holder is attached to the outer panel, and a wire with a plug to connect the unit to the household network is attached to the back panel.
How to assemble a welding unit with your own hands, demonstrates the video in our article.
In no case should the elements of the unit be fixed close to each other, so they must be blown.
On the sides of the frame, it is necessary to make holes from where air will flow. This is also necessary for installing a cooling system.
If the welding unit is constantly in the same place, then something is unlikely to happen to it.
For a long time, the current regulator will be able to work, more precisely, its handle, fixed on the outer wall.
But portable mini inverters that are taken to field work can be subjected to mechanical shock. Basically, the body of the product suffers from this, but there is a risk of the throttle falling off.
The product is assembled - it's time to check how it functions. When testing the operation of the welding unit, do not use temporary wires.
You need to check the product already with standard contact cables.
During the very first connection to the network, they look at the current regulator. It is important to see if there are any unfixed parts left.
If the unit is serviceable and free of defects, then you can start welding in various modes.
There are many types of welding machines, among which the following are best known: mechanical welding devices using consumable electrodes; equipment for argon-arc welding with non-consumable electrodes; for welding using flux with automatically consumable electrodes. In addition, there are generators for welding, transformers, inverters and devices for resistance spot welding. To work with each type of metal, well-defined electrodes are provided.
In terms of its design, an apparatus for working with direct current is much more complicated than an alternating current unit, since a rectifier with a diode or thyristor bridge is installed in it to obtain a constant voltage at the output. However, the power of the welding machine at the output is much less than that consumed due to its drop on the rectifier itself.
In other words, its efficiency is low, and this is a serious disadvantage in terms of energy savings. However, due to the stable arc and the ability to work with various metals, it could be classified as a professional equipment.
AC welding machine - what is its feature?
Much cheaper than the previous model AC welding machine, also working with consumable electrodes. It is great for working with ferrous metals, allows you to weld them with an overlap and butt.
If this welding machine is used, 220 volts is the operating voltage, however, at idle, it may vary depending on the electrodes used, which can be either calcium fluoride or rutile coated. The device is very easy to operate, provides for smooth adjustment of the current strength, which depends on the electrode chosen for operation.
This transformer welding machine can be successfully used both at home and in the factory. Electric welding machines are designed to operate from a 220 or 380 volt network and are respectively called single- or three-phase. Depending on this, the scheme for connecting welding wires changes.
The single-phase welding machine is connected by connecting one welding wire to the “phase”, the other to the “neutral” connector and the third to the “zero” ground. Otherwise, a three-phase welding machine is connected. Two ends of the welding cable are connected to any two "phases", and the third - to the protective "zero".
It should be noted that if a 380 volt welding machine is used, then it is considered more powerful than one connected to a 220 volt network, but this is not the only way to increase productivity.
Inverters - increase the power of the welding machine
So far, we have considered welding machines in which a conventional power transformer is used as an input voltage converter. It is he who determines the solid dimensions and heavy weight of this type of equipment. However, it is reliable and inexpensive.
But there are other types of devices in which the so-called inverters- semiconductor amplifiers. Small dimensions and weight have made them perhaps the most popular type of welding units.
With an efficiency level of up to 85%, the device works with different metals, guaranteeing high speed, quality and accuracy of welding. Inverter devices have different power and can be connected to both 220 and 380 volt networks.
DC welding (TIG DC)- this is one of the types of argon-arc welding, which is used for high-quality joining of most metals that do not form a refractory oxide film on the surface of the product during the melting process.
Principle of operation welding machines with direct current (TIG DC) is based on pulse-width modulation or PWM. The inverter circuit is represented by powerful transistors that rectify the mains voltage and convert it into an alternating high-frequency voltage up to 100 kHz. Further, the voltage is supplied to the primary winding of the transformer, and from the secondary winding the high-frequency alternating voltage is converted into a constant voltage.
TIG welders can weld with both "straight" and "reverse" polarity. "Direct" polarity is used for high-quality welding of titanium, high-alloy steel and other metals. With "straight" polarity, there is a minimum heating of the electrode and maximum penetration of the metal being processed. With “reverse” polarity, TIG machines allow using cathode sputtering to remove the oxide film (Al2O3), which is formed during the welding of aluminum and other refractory metals. However, in this case, due to the strong heating of the electrode, the tungsten electrode quickly burns out.
Arc excitation when working with TIG DC devices occurs between the metal and the tungsten electrode, to which the welding current is applied. At the same time, a protective gas (argon) is supplied to the welding zone through special nozzles in the TIG torch, which creates a shell and excludes the influence of the atmosphere on the formation of the seam.
Modern welding equipment of the TIG DC series is used for processing products made of high-alloy and stainless steels, carbon and medium-alloy steels, titanium and copper, zinc, alloys based on them and other metals.
Universal TIG DC machines are used for repair and production work, in the field of construction, in the manufacture of ventilation and heating systems, in the chemical and food industries, in machine tool building, in the production of pipelines, etc.
Advantages of DC welding (TIG DC):
- high quality of welding connection;
- no spattering of metal;
- the ability to perform welding in any spatial position;
- absence of slag formations;
- practically no seam modification is required;
- excellent visual control of the welding arc and seam formation.
- Welding experience required
- the difficulty of welding outdoors in strong winds or drafts;
- use of a gas cylinder with argon;
- low performance.

20 years ago, at the request of a friend, he assembled a reliable welder to work from a 220 volt network. Before that, he had problems with his neighbors due to a voltage drop: he needed an economical mode with current control.
After studying the topic in reference books and discussing the issue with colleagues, I prepared an electrical thyristor control circuit and mounted it.
In this article, based on personal experience, I tell you how I assembled and set up a DC welding machine with my own hands based on a home-made toroidal transformer. It turned out in the form of a small instruction.
I still have the scheme and working sketches, but I can’t give photographs: there were no digital devices then, and my friend moved.
Versatile Capabilities and Tasks
A friend needed an apparatus for welding and cutting pipes, angles, sheets of different thicknesses with the ability to work with electrodes 3 ÷ 5 mm. About welding inverters at that time did not know.
We settled on the design of direct current, as a more universal one, providing high-quality seams.
The negative half-wave was removed with thyristors, creating a pulsating current, but they did not begin to smooth out the peaks to an ideal state.

The welding output current control circuit allows you to adjust its value from small values for welding up to 160-200 amperes, which are necessary when cutting with electrodes. She:
- made on a board of thick getinaks;
- closed with a dielectric casing;
- mounted on the housing with the output of the adjusting potentiometer handle.
The weight and dimensions of the welding machine turned out to be smaller compared to the factory model. They placed it on a small cart with wheels. To change jobs, one person freely rolled it without much effort.
The power wire through an extension cord was connected to the connector of the introductory electrical panel, and the welding hoses were simply wound around the body.
Simple structure of DC welding machine
According to the principle of installation, the following parts can be distinguished:
- homemade transformer for welding;
- its power supply circuit from the network 220;
- output welding hoses;
- power unit of the thyristor current regulator with an electronic control circuit from the pulse winding.

The pulse winding III is located in the power zone II and is connected through the capacitor C. The amplitude and duration of the pulses depend on the ratio of the number of turns in the capacitance.
How to make the most convenient transformer for welding: practical tips
Theoretically, any model of transformer can be used to power the welding machine. The main requirements for it:
- provide arc ignition voltage at idle;
- reliably withstand the load current during welding without overheating of the insulation from prolonged operation;
- meet the requirements of electrical safety.
In practice, I have come across different designs of home-made or factory transformers. However, they all require an electrical calculation.
I have been using a simplified technique for a long time, which allows you to create fairly reliable designs for a medium-precision transformer. This is quite enough for domestic purposes and power supplies for amateur radio devices.
It is described on my website in the article This is an average technology. It does not require specification of grades and characteristics of electrical steel. We usually do not know them and cannot take them into account.
Features of the manufacture of the core
Craftsmen make magnetic wires from electrical steel of various profiles: rectangular, toroidal, double rectangular. They even wind coils of wire around the stators of burned out powerful asynchronous electric motors.
We had the opportunity to use decommissioned high-voltage equipment with dismantled current and voltage transformers. They took strips of electrical steel from them, made two rings out of them - donuts. The cross-sectional area of each was calculated to be 47.3 cm 2 .
They were isolated with varnished cloth, fastened with a cotton ribbon, forming the figure of a lying eight.

A wire was wound on top of the reinforced insulating layer.
Secrets of the power winding device
The wire for any circuit must be with good, durable insulation, designed for long-term operation when heated. Otherwise, during welding, it will simply burn out. We proceeded from what was at hand.
We got a wire with varnish insulation, covered with a fabric sheath on top. Its diameter - 1.71 mm is small, but the metal is copper.
Since there was simply no other wire, they began to make the power winding out of it with two parallel lines: W1 and W'1 with the same number of turns - 210.
The core bagels were mounted tightly: so they have smaller dimensions and weight. However, the flow area for the winding wire is also limited. Installation is difficult. Therefore, each half-winding of the power supply was smashed into its rings of the magnetic circuit.
In this way we:
- doubled the cross section of the power winding wire;
- saved space inside the bagels to accommodate the power winding.
Wire Alignment
You can get a tight winding only from a well-aligned core. When we removed the wire from the old transformer, it turned out to be twisted.
Figured out the required length. Of course, it wasn't enough. Each winding had to be made from two parts and spliced with a screw clamp right on the donut.
The wire was stretched on the street along its entire length. They took the pliers in hand. They clamped opposite ends with them and pulled with force in different directions. The vein turned out to be well aligned. They twisted it into a ring with a diameter of about a meter.
Technology of winding wire on a torus
For the power winding, we used the rim or wheel winding method, when a large-diameter ring is made from the wire and wound inside the torus by rotating one turn at a time.
The same principle is used when putting on a winding ring, for example, on a key or key chain. After the wheel is brought inside the donut, they begin to gradually unwind it, laying and fixing the wire.
Alexey Molodetsky showed this process well in his video "Winding a torus on a rim".
This work is difficult, painstaking, requires perseverance and attention. The wire must be tightly laid, counted, control the process of filling the internal cavity, keep a record of the wound number of turns.
How to wind a power winding
For her, we found a copper wire of a suitable section - 21 mm 2. Figured out the length. It affects the number of turns, and the open-circuit voltage necessary for a good ignition of the electric arc depends on them.
We made 48 turns with an average output. In total, there were three ends on a donut:
- middle - for direct connection of the "plus" to the welding electrode;
- extreme - to thyristors and after them to ground.
Since the donuts are fastened and the power windings are already mounted on them along the edges of the rings, the winding of the power circuit was performed using the “shuttle” method. The aligned wire was folded into a snake and pushed for each turn through the holes of the donuts.
The tapping of the middle point was performed by a screw connection with its insulation with varnished cloth.
Reliable welding current control circuit
Three blocks are involved in the work:
- stabilized voltage;
- formation of high-frequency pulses;
- separation of pulses on the circuit of control electrodes of thyristors.
Voltage stabilization
An additional transformer with an output voltage of about 30 V is connected from the power winding of the 220 volt transformer. It is rectified by a diode bridge based on D226D and stabilized by two D814V zener diodes.
In principle, any power supply with similar electrical characteristics of the output current and voltage can work here.

Impulse block
The stabilized voltage is smoothed by capacitor C1 and fed to the pulse transformer through two bipolar transistors of direct and reverse polarity KT315 and KT203A.


Transistors generate pulses on the primary winding Tr2. This is a toroidal type pulse transformer. It is made on permalloy, although a ferrite ring can also be used.
The winding of three windings was carried out simultaneously with three pieces of wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm. Made in 50 turns. The polarity of their inclusion matters. It is shown as dots in the diagram. The voltage on each output circuit is about 4 volts.
Windings II and III are included in the control circuit of power thyristors VS1, VS2. Their current is limited by resistors R7 and R8, and part of the harmonic is cut off by diodes VD7, VD8. We checked the appearance of the pulses with an oscilloscope.
In this chain, the resistors must be selected for the voltage of the pulse generator so that its current reliably controls the operation of each thyristor.
The trigger current is 200 mA and the trigger voltage is 3.5 volts.

On alternating current, it is only possible to weld ordinary mild steel (except for welding with an oscillator). In practice, there are many cases of welding parts made of cast iron, medium and high carbon steel, non-ferrous metals, and alloy steel. This requires direct current. The fact is that the electrodes for the above metals stably burn mainly on direct current. In addition, the use of an arc of direct or reverse polarity provides additional technological advantages.
Professional welding of pressure vessels is also carried out with direct current.
Scheme of a homemade DC welding machine


Transformer Tr 1 - ordinary welding, without any alterations. It is better if it has a rigid characteristic, that is, the secondary winding is wound on top of the primary. Diodes D 1 - D 4 - any, designed for a current of at least 100 A.
Radiators of diodes are selected in such an area that the heating of the diodes during operation does not exceed 100 ° C. A fan can be used for additional cooling.
Capacitor C1 is a composite of oxide capacitors with a total capacity of at least 40,000 microfarads. Capacitors can be used of any brand with a capacity of 100 microfarads each, including them in parallel. The operating voltage is at least 100 V. If such capacitors overheat during operation, then their operating voltage should be taken at least 150 V. Capacitors of other ratings can also be used.

If you plan to work only at high currents, then you can not install capacitors at all. Inductor Dr 1 is the usual secondary winding of a welding transformer. It is desirable that the core be made of rectangular plates. No bias current flows through it. If a toroidal core is used, then it is necessary to saw through the magnetic gap in it with a hacksaw.

Resistor R 1 - wire. You can use steel wire with a diameter of 6 - 8 mm and a length of several meters. The length depends on the secondary voltage of your transformer and the current you want to get. The longer the wire, the less current. For convenience, it is better to wind it in the form of a spiral.
The resulting welding rectifier allows you to weld straight and reverse polarity.
Welding of direct polarity - “minus” is applied to the electrode, “plus” to the product.
Reverse polarity welding - “plus” is applied to the electrode, “minus” to the product (shown in Fig. 4. 1.).
If the transformer Tr 1 has its own current regulation, then it is best to set the maximum current on it, and extinguish the excess current with the resistance R 1.
Cast iron welding
The practice of private welders has worked out two reliable and efficient ways of welding cast iron.
The first is used for welding products of a simple configuration, where the cast iron can “stretch” after the cooling seam. It should be borne in mind that cast iron is an absolutely non-ductile metal, and each cooling seam causes a transverse shrinkage of about 1 mm.
In this way, it is possible to weld a fallen off eye of the bed, a cast-iron body that bursts in half, and so on.

Before welding, the crack is cut with a V-shaped groove for the entire thickness of the metal.
You can weld the cut with any electrode, although the best results are obtained by welding with an electrode of the UONI brand (with any numbers) at a direct current of reverse polarity.
Overlays should be welded in all possible places. The more of them, the stronger the welded joint. Weld overlays should be along the current force.
Welded structures with overlays are often stronger than the original cast iron.
The second method was developed for products of complex configuration: cylinder blocks, crankcases, and so on. Most often it is used to eliminate the leakage of various liquids.

Before welding, the crack is cleaned of dirt, oil, rust.
For welding, a copper electrode of the brand "Komsomolets" with a diameter of 3 - 4 mm is used. The current is constant reverse polarity.
Before welding, a crack or patch is placed on spot tacks.
Welding is carried out with short seams randomly. The first seam is performed anywhere. Its length is not more than 3 cm.
Immediately after welding the seam, it is intensively hammered.
The cooling seam decreases in size, and forging, on the contrary, distributes it. Forging is performed for about half a minute.
Then wait for the metal to cool completely. Cooling is controlled by hand. If touching the seam does not cause pain, a second short seam of the same length is welded.
The second and all subsequent seams are welded as far as possible from the previous ones. After welding of each short seam, forging and cooling takes place.
The last to weld the closing sections between the short seams. The result is a continuous seam.
Determination of steel grade by spark
In repair practice, there are quite a lot of cases of welding steels that are unknown in chemical composition. Without determining the composition of such steels, their high-quality welding is impossible.
There is a way to determine the carbon content in steel with an accuracy of ±0.05%. It is based on the contact of the tested metal with a rotating emery wheel. The shape of the sparks formed in this case can be used to judge both the percentage of carbon and the presence of dopants.
The carbon in the separated metal particles burns out, forming flashes in the form of stars. Asterisks characterize the carbon content of the steel being tested. The higher the carbon content in it, the more intensely the carbon particles burn and the greater the number of stars (Fig. 4. 7.).
It is desirable to carry out such a test on a carborundum wheel with a grain size of 35 - 46. The rotation speed is 25 - 30 m / s. The room must be dark.
1 - the spark looks like a light, long, straight line with two thickenings at the end, of which the first is light and the second is dark red. The entire beam of sparks is light and has an oblong shape;
2 - new light sparks begin to separate from the first thickening. The beam of sparks becomes shorter and wider than the previous one, but also light.
3 - a beam of sparks is shorter and wider. A whole sheaf of light yellow sparks separates from the first thickening;
4 - at the ends of the sparks separating from the first thickening, brilliant white stars are observed;
5 - long reddish sparks are formed with characteristic separating stars;
6 - a long intermittent (dotted) spark of dark red color with a light thickening at the end;
7 - double intermittent (dotted) spark with light thickenings at the ends, thick and long - red, thin and short - dark red;
8 - the spark is the same as in paragraph No. 7, with the only difference that the sparks have a gap.

Training in the spark test method should begin with samples of known steel grades.
When applying this method, it should be borne in mind that steel in a hardened state gives a shorter spark beam than unhardened steel.
A spark test must be taken at a depth of 1–2 mm from the surface, since there may be a decarburized layer on the metal surface.
In contact with the emery wheel of non-ferrous metals and their alloys, in which carbon is absent, no sparks are obtained.
Welding of medium and high carbon steels
Medium carbon steels are welded with low carbon electrodes. The depth of penetration should be small, therefore, a direct current of direct polarity is used. The current value is selected reduced.
All these measures reduce the carbon content in the weld metal and prevent the occurrence of cracks.
For welding use electrodes UONI-13/45 or UONI-13/55.
Some products must be heated to a temperature of 250 - 300°C before welding. Full heating of the product is best; if this is not possible, then apply local heating with a gas burner or cutting torch. Heating to a higher temperature is unacceptable, as it causes cracks due to an increase in the depth of penetration of the base metal and the resulting increase in the carbon content in the weld metal.
After welding, the product is wrapped with a thermally insulating material and allowed to cool slowly.
If necessary, after welding, heat treatment is carried out: the product is heated to a dark cherry color and slow cooling is provided.
High carbon steel is the hardest to weld. Welded structures are not made from it, but welding is used in repair production. For welding such steel, it is best to use the same methods as described earlier for welding cast iron.
Manganese steel welding
Manganese steel is used for parts with high wear resistance: excavator buckets, excavator bucket teeth, railway crosses, stone crusher necks, tractor tracks, and so on.
For welding, electrodes TsL-2 or UONI-13nzh are used.
Welding current is selected at the rate of 30 - 35A per 1 mm of electrode diameter.
Welding generates a large amount of gases. To facilitate their exit from the molten metal, surfacing should be carried out with wide beads and short sections, otherwise the weld will be porous.
Forging is required immediately after welding.
To increase the hardness, strength, toughness and wear resistance of the surfacing, it is necessary, after applying each bead, while it is still heated to red heat, to harden with cold water.
Chrome steel welding
Chromium steels are used as stainless and acid-resistant for the manufacture of equipment for the oil refining industry.
Welding of chromium steels must be carried out with preheating to a temperature of 200 - 400 ° C.
When welding, a reduced current strength is used at the rate of 25 - 30 A per 1 mm of the electrode diameter.
Apply electrodes TsL-17-63, SL-16, UONI-13/85 on direct current of reverse polarity.
After welding, the product is cooled in air to a temperature of 150 - 200°C, and then tempered.
Tempering is carried out by heating the product to a temperature of 720 - 750 ° C, holding at this temperature for at least an hour and then slowly cooling in air.
Welding of tungsten and chrome tungsten steel
This steel is used to make cutting tools.

Using welding, a cutting tool can be made in two ways:
1) welding of finished high speed steel plates onto a mild steel holder;
2) surfacing of high-speed steel on mild steel.
Finished plates are welded in the following ways:
1) using contact welding;
2) using argon welding with a non-consumable electrode;
3) using gas brazing with high temperature solder;
4) consumable DC electrode.
For surfacing, high-speed steel waste can be used: broken drills, cutters, countersinks, reamers, etc.
These wastes can be deposited using gas or argon welding, as well as making electrodes for electric arc welding from them.
After surfacing, the tool is annealed, processed mechanically, then subjected to triple quenching and tempering.
High alloy stainless steel welding
Stainless steel in everyday life has found a fairly wide application: various containers, heat exchangers, water heaters are made from it. Used in private baths as heat-resistant.

It is possible to distinguish such steel from ordinary steel by three characteristic features:
1) "stainless steel" is distinguished by a light steel color;
2) when a permanent magnet is applied, it is not attracted, although there are exceptions;
3) when processed on an emery wheel, it gives few sparks (or does not give at all).
Stainless steel has a high coefficient of linear expansion and a low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
The increased coefficient of linear expansion causes large deformations of the welded joint up to the appearance of cracks. Some welded structures made of "stainless steel" before welding, it is desirable to heat up to a temperature of 100 - 300 ° C.
A low coefficient of thermal conductivity causes a concentration of heat and can lead to burn-through of the metal. Compared to welding ordinary steel of the same thickness, when welding stainless steel, the current is reduced by 10 - 20%.

For welding, a direct current of reverse polarity is used.
Use electrodes brand OZL-8, OZL-14, ZIO-3, TsL-11, TsT-15-1.
One of the main conditions for welding is to maintain a short arc, this provides better protection of the molten metal from oxygen and nitrogen in the air.
Corrosion resistance of seams increases with their accelerated cooling. Therefore, immediately after welding, the seams are watered. Pouring with water is permissible only for steel that does not crack after welding.
Welding of aluminum and its alloys
Welding with coated electrodes is used for aluminum and alloys with a thickness of more than 4 mm.
OZA-1 brand electrodes are used for welding technical aluminum.
OZA-2 electrodes are used for welding casting defects.
Recently, OZA brand electrodes have been replaced by more advanced OZANA brand electrodes.
Coating of electrodes for aluminum welding strongly absorbs moisture. When storing such electrodes without moisture protection, the coating can literally drain from the rod. Therefore, such electrodes are stored in a plastic case with moisture absorption means. Before welding, they are additionally dried at a temperature of 70 - 100 ° C.
Before welding, aluminum parts are degreased with acetone and cleaned to a shine with a metal brush.
Welding is carried out on a direct current of reverse polarity.
Welding current 25 - 32 A per 1 mm diameter of the electrode rod.
Before welding, the part is heated to a temperature of 250 - 400°C.
Welding must be carried out continuously with one electrode, since the slag film on the part and the end of the electrode prevents the arc from re-igniting.
If possible, linings are laid on the back of the seam (see aluminum gas welding).
Arc welding produces seams of medium quality.
Welding of copper and its alloys
Pure copper lends itself well to welding, and it is recommended to cook it in two ways. The welding method depends on the thickness of the part.
With a product thickness of not more than 3 mm, it is best to use carbon electrode welding. Welding is performed with direct current of direct polarity with an arc length of 35 - 40 mm.
An electrical wire can be used as a filler material. Do not forget to clean it from insulation before welding.
To improve the quality of the weld, a flux is applied to the edges to be welded and to the filler wire, consisting of 95% calcined borax and 5% metallic magnesium powder. You can use one borax, but the results will be worse. If a high quality weld is not required, the flux is not used.
Arc Welding Safety
Electric arc welding has several factors harmful to the health of the welder: electric voltage, electric arc radiation, gases, sparks and metal splashes, thermal heating, drafts.
The maximum permissible open circuit voltage of the welding transformer is 80 V, and the welding rectifier is 100 V. In dry weather, this voltage is practically not felt, but in humid conditions, a rather noticeable tingling of the hand begins. The same can be observed when the welder is on the metal part being welded, and even more so inside it.
When welding in wet weather, as well as standing on metal, regardless of the weather, it is necessary to use rubber gloves, a rubber mat, rubber galoshes. Gloves, rug and galoshes should be made of dielectric rubber, that is, the one used by electricians. Rubber products sold for domestic use are not electrically insulating.
Protective grounding is used to protect the welder from accidental breakdown of the transformer. The grounding device is described in Chapter 1.
To reduce the possibility of electric shock, it is best to use transformers with a low open-circuit voltage.
Protection against arc radiation is a welder's suit, a mask with a set of glasses, and gloves. Always fasten the top collar of the suit, otherwise you will have an indelible “tie”.
The ultraviolet radiation of the arc is reliably attenuated by a 10 m air column, so do not let anyone get closer than 10 m to the welding site (especially children!).
The composition of the coating of the electrodes includes gas-forming substances, so the coated electrodes smoke heavily. The only way to protect against smoke is forced ventilation. The arrangement of such ventilation is described in Chapter 1.
Another unfavorable factor in the work of a welder is associated with ventilation - drafts. The load of the welder during work is most often static, that is, the welder works almost motionless. In this case, there is no self-heating of the body, which can lead to hypothermia.
As the experience of many welders shows, no draft hardening helps. More reliable protection is warm clothing, especially around the waist (the welder works bent over).
Warm clothes can also have a negative effect. When switching to a dynamic load, the welder begins to sweat, sweat, together with a draft, causes a guaranteed cold.
The best option to avoid a cold is to install a supply fan heater. It should heat the supply air to above zero temperature even in severe frost. If you prefer not to work in such frosts, then the fan power is sufficient at 3 kW.
Metal splashes are considered quite an unpleasant phenomenon. Getting on a suit, in shoes, they cause smoldering of protective clothing or a fire if combustible substances are nearby. Get leather protective clothing and tarpaulin boots - and you will adequately protect your body.
When welding at high currents and arc cutting metal, the electrode holder, welding wires and welding mask may overheat. Therefore, do not touch the metal parts of the mask with your face, but put a heat-insulating sleeve on the holder handle. Regularly check all wire connections - they can cause a fire.
The above rules apply to other types of electric welding: argon, semi-automatic, contact.